

And so the electron configuration here for calcium with a positive two charge, this calcium cation, is going to be the electron configuration In that 4s sub-shell, in the fourth shell, are gonna go away. Now what do you think is going to happen if we were to lose two electrons? Well those two electrons Let me do this in a new color, let's call this 4s two. And so we're going to have argon and then we're going to have, To have two electrons for that fourth shell. For neutral atoms, the 6p atomic orbitals should be higher in energy than. So it's going to have theĮlectron configuration of argon and then we are going Which of the following electronic transitions for a one electron atom or ion. Neutral calcium, the noble gas that comes right before calcium is argon. And so neutral calcium, you could view it, actually let's do it in The electron configuration of a neutral calcium atom and then from that, we can take two of the highest energy electrons away. To figure this out is first we could figure out What would be its electron configuration? Pause this video and All orbits except the last orbit are completely filled. The last electron during configuration occupies p orbital, hence these elements are p block elements. They have characteristic outer orbit configuration of ns2 np5. You could do this as a neutral calcium that has lost two electrons. Radial (total) probability of finding an electron in the 1s orbital of a hydrogen atom is. All halogens contain seven electrons in their outermost shell. Out the electron configuration of a part positively charged calcium ion. Of 1s two, 2s two, 2p, now it's going to have anĮxtra electron here, 2p six. So the fluoride anion is going to have an electron configuration The fluorine has nabbedĪn electron from someplace and so where will that extra electron go? Well our 2p sub-shell has Pause this video and try to figure it out. The maximum number of electrons in d-orbital of an element with atomic number 46 is. So if that's the electronĬonfiguration for fluorine, what do you think theĮlectron configuration for fluoride would be? This is just the anion that Three four five electrons in that 2p sub-shell. And we are going to have, we're talking about a neutral fluorine, we are going to have one two
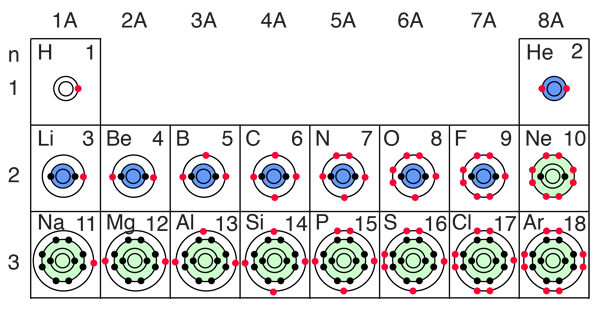
Has nine electrons, and we could just use our x-ray spectroscopyanalysis of x rays emitted from a target hit by an electron beam (Instrumental Methods: X Rays, Atomic Numbers, and Orbital Structure.
The electron configuration of a neutral fluorine atom? All right, now let's work Little bit of practice, try to pause this video and think about what is the halogen with electrons in the 6p atomic orbitals.2 answers 0 votes: i still dont understand.especially part a, because element number 116 is not on the. Neutral fluorine atom's electron configuration would be. an element with three unpaired 5d electrons c. from the atomic 6s populations of the molecular orbitals on the gold ion. Let's just start looking at some examples. The total electron density at the nucleus p(0) depends on the nature of the. In many videos we have already talkedĪbout electron configuration and now in this video we're going to extend that understanding by thinking about the electronĬonfiguration of ions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
